An rSr pattern in leads V1-V2 can be observed when ECG leads are placed in the 2nd intercostal space. And the caveats of improper lead positioning were recently reviewed.

How To Perform And Interpret Provocative Testing For The Diagnosis Of Brugada Syndrome Long Qt Syndrome And Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology
The type 2 ST-segment elevation has a saddleback appearance with a high takeoff ST-segment elevation.

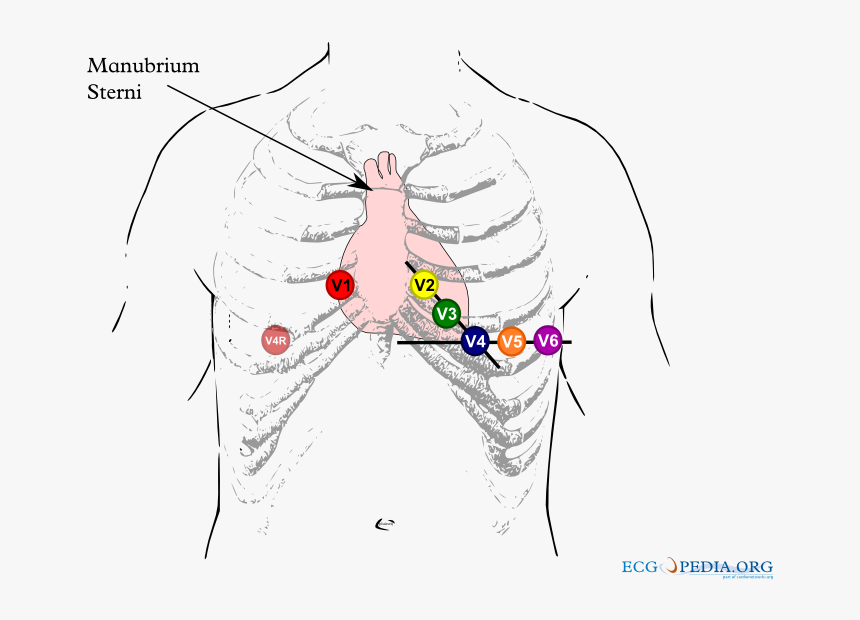
. Brugada_lead_placementpng 800 600 pixels file size. Proper precordial ECG lead placement is paramount. Consider as cause of syncope in patients with family history of sudden death.
First described in 1992 by the Brugada brothers the disease has since had an exponential rise in the numbers of cases reported. Brugada Syndrome is an ECG abnormality with a high incidence of sudden death in patients with structurally normal hearts. Recently three criteria analyzing the ST segment and r width to identify true Brugada pattern ECGs have been described.
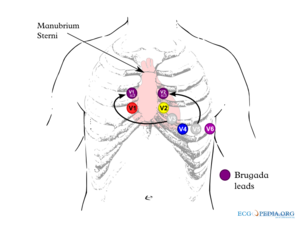
Brugada Type 2 Not Type 1 V1 and V2 may be placed in the 3 rd or even 2 nd intercostal spaces in order to elicit a type 1 Brugada pattern and is considered diagnostic. This ECG was recorded. V1 and V2 should be placed at the 4th intercostal space.
High take-off of the descending limb of the r at least 2 mm above the isoelectric line in our case it is greater than 2 mm. Imagepng This file is from a shared repository and may be used by other projects. By contrast a type 2 Brugada pattern may often be found with these high leads are applied to healthy people especially in fit young males.
Refer to Figure 1. ECG recordings and even more with placement of precordial leads V1V2 and V3 in the 2 nd and 3 rd intercostal space which may bring out a typical Brugada pattern and should be routinely performed when the diagnosis is suspected but is uncertain on a standard ECG and in screening of family members of BS patients. Mismatch between QRS duration in leads V1 and V6 longer in lead V1.
Distinguishing between a saddle back Type 2 Brugada pattern and one of many Brugada-like patterns presents challenges especially in athletes. Detection of the Brugada pattern in the RPLs in either a horizontal or vertical orientation seems arbitrary as ECG lead placement is based on anatomical considerations and recordings from the third or fourth intercostal space are likely to record similar electrical activity. The mean age of sudden death is 41 with the age at diagnosis ranging from 2 days to 84 years.
The diagnosis of the BrS is mainly based on the presence of a spontaneous or Na channel blocker induced characteristic electrocardiographic ECG pattern type 1 or coved Brugada ECG pattern typically seen in leads V1 and V2. Brugada Syndrome is a rare inherited cardiac arrhythmia syndrome that is characteristed by a coved-shaped atypical right bundle branchpattern on a 12-lead ECG Type-1 Brugada pattern ECG and is associated with ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Type 2 Brugada syndrome.
Placement of the right precordial leads in a superior position up to the second intercostal space above normal can increase the sensitivity of the ECG for detecting the Brugada phenotype both in the presence or absence of a drug challenge. 84 KB MIME type. The terminal portion of the ST segment is elevated 1 mm.
It has been recognized as a clinical entity since 1992. Note the coved type ST segments in the right precordial ECG leads note V3 is placed in the 3rd intercostal space above V1 V1ic3 and V5 is placed in the 3rd intercostal space above V2 V2ic3. The specificity was 100 one-sided 975 CI.
12 to ensure consistent lead placement we incorporated a high precordial lead v1 and v2 at the 2nd intercostal space ecg into our. Careful placement of leads is essential to avoid false positive findings. Conclusion In our athletes without preexisting incomplete RBBB a Brugada-like pattern was easily obtained and highly prevalent with high placement of anterior precordial leads.
However errors in placement of ECG leads can create artifacts mimic pathologies and hinder proper ECG interpretation. 12-lead ECGs were recorded in a single male healthy subject in his mid. Electrocardiography is a very useful diagnostic tool.
It meets or at least nearly meets criteria for type 2 Brugada. Please see the file description page for further information. The reciprocal STT wave change is not recognized on ECG in Brugada syndrome.
Brugada syndrome is a rare inherited arrhythmic disorder causing an increased risk of syncope and sudden death due to ventricular fibrillation. Change of a normal ECG into a type-1 Brugada ECG during ajmaline challenge. Brugada ECG ST elevation in the right-side precordial leads Coved morphology RBBB or Incomplete RBBB Diagnosis Expect a normal physical examination.
The use of precordial leads in the 2nd or 3rd intercostal space has been described in patients with suspected and known brugada syndrome 5 11. Brugada Syndrome is an abnormal ECG Right Bundle Branch Block Pattern with coved ST elevation over the right precordial leads of V1-V3 which leads to ventricular fibrillation VF and sudden cardiac death SCD in patients with structurally normal hearts. Brugada syndrome is diagnosed in patients with type 2 or type 3 ST-segment elevation in 1 lead among the right precordial leads V1 V2 positioned in the 2nd3rd or 4th intercostal space when a provocative drug test with intravenous administration of class I antiarrhythmic drugs induces a type I EKG morphology 3.
Saddleback shaped ST segment elevation with J point elevated 2 mm in leads V1 andor V2. The physical exam should be used to rule out the influence of other cardiac causes of syncope. On the other hand ECG manifestations in Brugada syndrome patients represent persistent or fluctuating ST-segment elevation in the right precordial leads from V1 to V3 which is improved during exercise testing.
Having just written on this topic I knew that this could be the result of lead placement that is too high. This is the second of a two-part series discussing how to recognize and avoid these errors. A typical baseline Fig A and positive ECG Fig B are shown.
The type 1 Brugada ECG pattern is characterized by a complete or incomplete right bundle-branch block pattern with a coved morphology ST-segment elevation of at least 2 mm in the right precordial leads V 1 V 3 followed by a negative T wave. Note that the electrodes to lead V1 and V2 may be placed in the second third or fourth intercostal space in the pursuit of these ECG changes. The r -wave is thus not distinct as it is in benign causes of rSr 2.
There is rSr in both V1 and V2 with a saddleback in lead V2 and the beta angle is wide. Once these are fulfilled there should be in lead V2. No type 1 ECG patterns were identified but 16 47 subjects with a type 2 ECG and 32 94 subjects with a type 3 ECG were identified in any lead placement.
99 for the use of EEP-ECG to uncover type 1 pattern. Most patients with Brugada present with no symptoms. A number of criteria have been proposed to assess Brugada ECG patterns.
Manifestations of Brugada-type ECG 41. In total 43 13 subjects had any BrS ECG pattern in any lead placement. 80 of Brugada syndrome diagnosed only after a cardiac arrest.

Ecg Interpretation In Brugada Syndrome Sciencedirect

Ecg Interpretation In Brugada Syndrome Sciencedirect
Brugada Syndrome Ecg Placement Hd Png Download Kindpng

Brugada Syndrome Brs This Picture Displays The Ecg Trace Of A Download Scientific Diagram

Raviele Antonio On Twitter Figure Showing The Value Of High V1 V2 Leads Placement To Unmask Type 1 Brugada Ecg Pattern Dr Santangeli Abollmannmd Ecgtalk Adribaran Drfermingarcia Jorgeeromeromd Lluismont2 Manliomarquez Drjasonandrade

Positioning Of High Precordial Leads Hv1 To Hv6 For Procainamide Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment